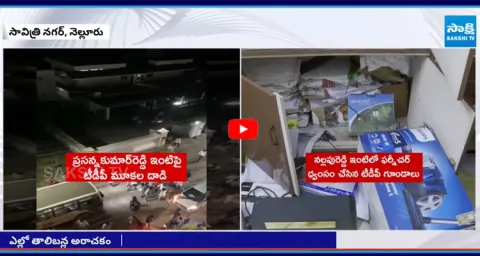
ఒక తీవ్రమైన ప్రభావం కనిపిస్తుంది ..?
Directions (Q. 1-10): Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given below it. Certain words have been printed in bold to help you locate them while answering some of the questions.
Directions (Q. 1-10): Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given below it. Certain words have been printed in bold to help you locate them while answering some of the questions.
Many factors influence whether you notice a pain at all and if you do, how much it hurts. Since the pain message is received and interpreted by the brain, competing messages may block it or other factors may enhance the intensity of the sensation. The pain threshold-the point at which a person reports-can be raised as much as 40% by hypnosis or by loud noise or other distractions.
Fully a third or pains can be relieved by a placebo, or sugar pill, if the patient believes it to be an active pain-killing drug. Recent studies suggest that placebos work by trig-gering the release of the body's own morphine endorphins. That a pain can be dissipated by a placebo does not mean that it was feigned. A placebo is anything that seems to be a "real" medical treatment - but isn't. It could be a pill, a shot, or some other type of "fake" treatment. What all placebos have in common is that they do not contain an active sub-stance meant to affect health. Some-times a person can have a response to a placebo. The response can be positive or negative. For instance, the person's symptoms may improve. Or the person may have what appears to be a side effect from the treatment.
These responses are known as the "placebo effect." Research on the placebo effect has focused on the relationship of mind and body. One of the most common theories is that the placebo effect is due to a person's expectations. If a person expects a pill to do something, then it's possible that the body's own chemistry can cause effects similar to what a medication might have caused.
For instance, in one study, people were given a placebo and told it was a stimulant. After taking the pill, their pulse rate sped up, their blood pressure increased and their reaction speeds improved. When people were given the same pill and told it was to help them get to sleep, they experienced the opposite effects.
Experts also say that there is a relationship between how strongly a person expects to have results and whether or not results occur. The stronger the feeling, the more likely it is that a person will experience positive effects. There may be a profound effect due to the interaction between a patient and health care provider.
1. A pain may be felt lightly or intensely by a person according to
1) his brain capacity
2) how much it hurts
3) the intensity of other messages to the brain
4) the nature of the person and his attitude to pain
5) the nature of taking medicines
2. Loud noise is resorted to in red-ucing pain on the principle that
1) it can shock a person out of consciousness
2) it neutralizes the cause of the pain
3) the intensity of the pain sensation can be enhanced
4) the brain can be distracted from noticing the pain message.
5) It enhances the cause of pain
3. According to the passage
1) A placebo helps a doctor to detect whether a patient really has pain
2) Placebos help in relieving pain
3) Placebos immunize the body against pain
4) Doctors prescribe placebos in order to deceive their patients
5) None of these
4. Research on the placebo effect has focused on the study of
1) Pills that are given to patients
2) What doctors suggest the patients
3) The effect of this on mind and body
4) How the patient studies the case
5) Whether doctors can learn anything from this
5. What will have an intense effect on the patients?
1) The use of a drug
2) The use of pills or medicines which are related to the disease
3) Following their own will
4) Having an interaction with the health care provider
5) Feeling that it is not good
Directions (Q. 06-08): Choose the word which is MOST SIMILAR in meaning to the word printed in bold as used in the passage.
6. Threshold
1) Verge 2) Wedge 3) Wage
4) Gaze 5) Gauge
7. Distractions
1) Dimensions 2) Deputation
3) Diversions 4) Demands
5) Orders
8. Dissipated
1) Upright 2) Degenerate
3) Dissociate 4) Compact
5) Assemble
Directions (Q. 9-10): Choose the word which is MOST OPPOSITE in meaning to the word printed in bold as used in the passage.
9. Expectations
1) Follow 2) Promise
3) Profound 4) Despair
5) Lighten
10. Profound
1) Deep 2) Negative
3) Positive 4) Reflective
5) Superficial
Directions: (Q. 11-15): Re-arrange the following six sentences in proper sequence to form a meaningful paragraph than answer the questions given below them which are labeled as A, B, C, D, E and F to produce the correct sentence.
A. Once after a philosopher had given a lecture, a woman approached him.
B. The feeling that the world had to be on solid ground persisted to modern times.
C. Some early maps showed the earth to be resting on the backs of giant elephants.
D. The earth, she told him, rested on the back of a giant turtle.
E. The woman shouted, "It's no use! It's turtles all the way down!"
F. The philosopher asked her what the turtle stood on and she said, "a bigger turtle". The philosopher asked her the next logical question.
11. What is the FIRST sentence after rearrangement?
1) C 2) B 3) D 4) E 5) F
12. What is the SECOND sentence after rearrangement?
1) A 2) B 3) D 4) E 5) F
13. What is the FOURTH sentence after rearrangement?
1) A 2) C 3) D 4) E 5) F
14. What is the FIFTH sentence after rearrangement?
1) B 2) C 3) D 4) E 5) F
15. What is the LAST sentence after rearrangement?
1) A 2) B 3) D 4) E 5) F
Directions (Q. 16 to 20): Which of the phrases (1), (2), (3) and (4) given below each sentence should replace the phrase printed in bold in the sentence to make it grammatically correct? If the sentence is correct as it is given and no correction is required, mark (5) as the answer.
16. Raghu has not and can never be in the good books of his emp-loyer because he lacks sincerity.
1) has not and cannot be 2) has not and can never been
3) has not been and can never be 4) has not been can never been
5) No improvement
17. The logic of the Berlin Wall already had been undermined, but when the news came through that the wall itself had been opened I jumped into a car.
1) had been undermined already
2) had been already been undetermined
3) had been already undermined
4) had already been undetermined
5) No improvement
18. Other countries have wiped out this practice ten years ago.
1) wiped out 2) wipes out
3) did wipe 4) has wiped
5) No improvement
19. While we would like that all Indian children to go to school, we need to think why they do not.
1) that all the Indian children 2) if all the children of India
3) all Indian children 4) Indian all children
5) No improvement
20. If stood alone in defence of truth, and the whole world is banded against me and against truth, I would fight them all.
1) will be banded
2) were banded 3) banded
4) will band 5) No improvement
Directions (Q. 21-25): Read each sentence to find out whether there is any grammatical mistake/ error in it. The error, if any, will be in one part of the sentence. Mark the number of that part with error as your answer. If there is 'No error', mark (5) as your answer.
21. The wards of the hostel are (1)/ allowed to do (2)/ anything except to go out (3)/ on their own at night. (4)/ No error (5)
22. The best way to explore Egypt (1)/ is to take a trip down Nile, (2)/ the river that runs like a thread (3)/ throughout Egyptian history. (4)/ No error (5)
23. The hawkers have been carrying (1)/ out their business on the main (2)/ pavement since three years (3)/ but no one has ever objected. (4)/ No error (5)
24. Hardly I have finished (1)/ writing when my brother (2)/ snatched the fountain (3)/ pen from my hand. (4)/ No error (5)
25. India, which makes up (1)/ sixteen percent of the global population, (2)/ carries twenty percent (3)/ of their disease burden. (4)/ No error (5)